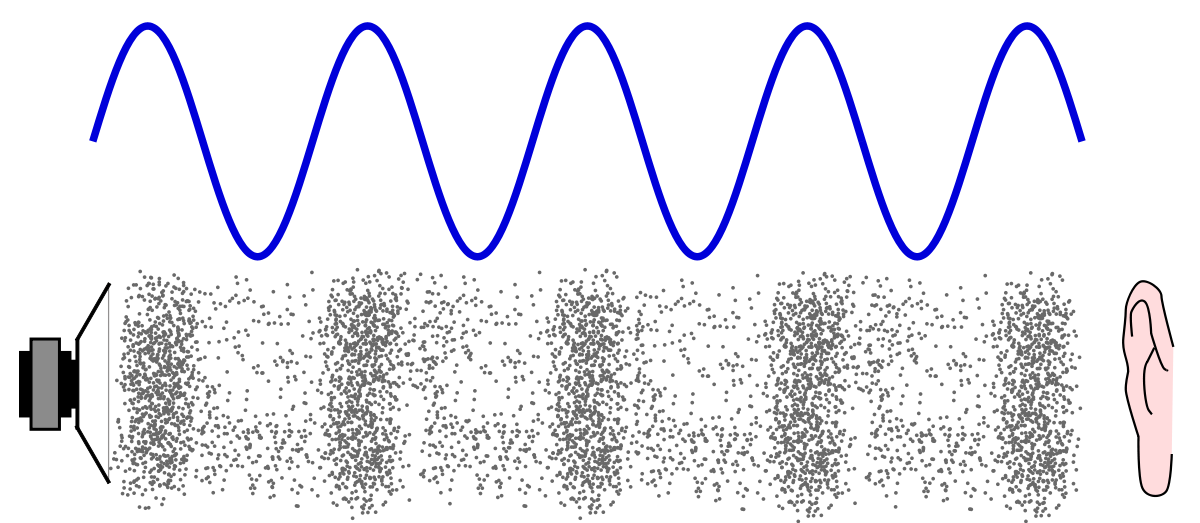
Sound is produced when sound
waves are emitted by a vibrating source and
they are propagated in a material medium with certain velocity.
Sound waves are longitudinal
waves with alternate compressions and rarefactions. Sound waves always require
a medium to travel and so they can never
travel in vaccum.
Propagation of
sound waves :-
- Transverse
Waves : – They have alternate crests
and troughs. Thus, their propagation involves change in shape of a body
(medium). As solids provide largest resistance to change of shape, so
transverse waves propagate best in solids.
- Longitudinal
Waves : – They have alternate
compressions and rarefactions. So, their propagation involves change in volume
or density of a body(medium). As volume or density can be changed in solids,
liquids or gases, so longitudinal waves can propagate in any of these mediums.
Sound Waves in different mediums
- Solids : Sounds coming
through walls, windows, floors etc of a building, sound of an approaching rail
when heard in rail tracks.Liquids : sound waves coming from submarines underwater.Gases : When we speak in air.
Speed of sound :- Speed of sound depends on the medium. It travels with different
velocities in different mediums.
Speed
of sound depends on :
- Nature of the
medium
- Temperature
- Atmospheric humidity
Speed of sound is generally
more in solids than in liquids or gases. This is because Restoring Force is very high in solids.
Note : – study the examples
yourself
- Horn of a car
- Lightning and thunder
- Hitting of ball
in cricket
Range of Hearing in Humans : –
Loudness : The
sensation produced in the ear which enables us to distinguish between a faint
sound and a loud sound.
Humans can hear sounds from
frequency 20 Hz to 20 Khz. This is known as Audible Range.
Ultrasonic Waves : Waves having frequency more than 20 khz are known as Ultrasonic
waves. Sound produced by these waves is known as UltraSound. Bats can produce
and hear ultrasonic waves, other examples are dogs, cats, some insects etc.
These organisms can hear sound of frequency below 20 Hz also.
Supersonic Waves : When an object travels with speed greater than speed of sound, then
it is said to have supersonic speed and waves produced are known as supersonic
waves. When supersonic aircrafts fly, then they produce these waves and then
they are known as Shock Waves.
Sonic Boom
: The sound produced due to shock waves. Shock waves are very high energy
waves. The sound produced is very unpleasant and can break glass panes and
produce pain in ears.
Reflection of Sound
Whenever
a sound wave hits an obstacle and reflects back, this phenomenon is called
ECHO. For reflection of sound we need attended objects a large obstacles.
Practical
Application of reflection of sound
1 MegaPhone : It is a horn-shaped instrument
(tube). This shape prevents spreading prevents spreading of sound waves and
allows multiple reflections of sounds. This concept is used in loud-speakers.
2 Hearing Aid : Persons who can’t hear
clearly use hearing aids. These hearing aids reflect sound inside the ear. This
enhances the amplitude of vibrating layer of air inside the air and helps in
improving hearing.
3 Sound Boards : These are concave shaped
boards that are placed behind the speaking area in a big auditorium. Speakers
are placed on the focus of this concave shape. Sound waves that originate from
this speakers reflects from the surface and move parallel to each other thus
not interfering with each other. This ensures better hearing at large
distances.
ECHOES
Reflection
back of sound from obstacles is called an echo.
The
sensation of sound remains in our brain for about 0.1 sec.
For an
echo, the sound waves should reach us after 0.1 sec of hearing that sound.
Velocity
of sound in air = 344 m/s
Distance travelled by waves = 344 X 0.1 = 34.4 m
Þ Distance of an obstacle should be = 34.4/2 = 17.2 m
Multiple Echoes : When waves
reflect from many surfaces repeatedly.
Rolling of Thunder :When thunder
occurs, the waves get reflected repeatedly from clouds, water vapours, dust
particles etc. This causes a rolling of Thunder.
SONAR
Sound Navigation And Ranging. This
principle is based on reflection of sound. Here, we use ultrasonic waves. The
main use of SONAR is to detect submerged submarines, rocks, sea bed (depth of
the ocean), hidden icebergs etc.
Total distance travelled = 2d
Velocity of wave = v
Time, t = 2d/v
d = vt/2
Notional Use of SONAR :-
It is
done by Bats. They use ultrasonic waves to find an obstacle in the way. They
hunt like that also for its prey. Using this, they know the distance of their
prey.
USES OF SONAR
- To find cavities
in metals.
- To find level of
a liquid in a metallic tank.
Applications
of ultrasonic waves
- Ultrasound is used to clean parts located in
hard-to-reach places. example- Spiral tube, odd shaped parts, electronic
components.
- In detecting cracks and flaws in metal blocks.
- Ultrasonic waves are made to reflect from various
parts of the heart. This technique is called ‘echocardiography’.
- Ultrasound scanner uses ultrasonic waves for getting
images of internal organs of the human body.
- Ultrasound is used in breaking small ‘stones’ formed
in the kidneys into fine grains.