Biology
Reproduction
CLASS X SCIENCE NOTES
REPRODUCTION
Reproduction– Is a biological process by which new individuals of the same species are produced by existing organisms (Parents)
SIGNIFICANCE – Essential for the Perpetuation of species.
TYPES OF REPRODUCTION
ASEXUAL SEXUAL
1 Off Spring arises from a simple Off spring arises from individuals individual parent (parents) a male & female 2 are exact copy of parents are the mixture of parents.
3 Asexual reproduction takes place in Take place in all higher plants & unicellular organisms, some plants animals & some animals like Hydra & sponges
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION– It is the mode of reproduction in which some body cells undergo separated mitotic divisions to form less or more new individuals of the same kind.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
1 Fission
2 Budding
3 Spore formation
4 Regeneration
5 Vegetative Propagation
Fission – The body of organisms divide into fragments & each fragment can give rise to a new individual.
It is of two types:-
Binary Fission Multiple fission
1 A unicellular organism is divided Body is divided into many into into two daughter cells. individuals
2 During this, nucleus divides into Nucleus divides into several times two nuclei followed by a constriction into many daughter nuclei in the cell membrance
3 This contruction gradually increases Daughter nuceli arrange along inwards and divides the cytoplasm the periphery of the parents cells into two parts
4 Two daughter cells are formed A bit of cytoplasm around each eg. Amoeba daughter nucleus develops and outer membrane Thus, a nucleated body divides into as many parts as the no. of daughter nuclei and forms daughter individuals eg. plasmodium
Budding-
(1) It is also a type of asexual reproduction
(2) Some of the body cells undergo repeated mitotic division to form a bulge.
(3) This lateral bulge is called bud
(4) Bud slowly enlarges to develop into a new individual on the body of parent
(5) Finally, it separates from the parent body & grows into a new individual this is called budding.
Budding in Yeast
1 A small protuberance appears on the upper part of an adult cell.
2 This protuberance gradually grows in size.
3 From this newly budded cell, another bud appears at the lip.
4 This process continues 3-4 times, resulting in a chain of yeast cells.
Spore Formation –
Most common method of Asexual Reproduction
e.g.:- fungi, bacteria(Rhizopus, Mucor Penicillum)
1 A round structure develops at the tip of fungal hypha called sporangium.
2 With in Sporangium, nucleus divides several times to form a no. of nuclei.
3 Each nucleus, then with a point of cytoplasm develops into a spare.
4 After the bursting of sporangium, spores are liberated and each spore develops into a new hypha after reaching ground.
Regeneration – Regeneration is defined as the ability of an organism to replace its lost body parts in some organisms help in reproduction e.g Hydra, Planaria, Sponges, spirogyra etc.
Regeneration in Hydra or Planaria – If the body of hydra or planaria gets cut into pieces a fragment is capable of regenerating into an entire individual
Vegetative Propagation – It is method of asexual reproduction in higher plants in which a new plant develops from the vegetative parts of plants like root, stem or leaf.
e.g 1.Vegetative propagation by roots – buds on roots of Guava
2 Vegetative Propagation by leaves – buds on leaves e.g Bryophyllum
3 Vegetative Propagation by stem – Onion, Banana, garlic, water hyacinth etc.
Three Methods of Vegetative Reproduction
Cutting –
(1) A part of plant is cut like stem root, leaf or bulb.
(2) When this cutting is placed in moist soil, gives out roots.
(3) After sometime, the cutting develops into a new plant, similar to parent plant e.g rose, grapes, sugarcane etc.
Layering
(1) A part of stem is pulled & buried in moist soil, while it is attached & supported by the parent, plant
(2) After sometime, the layered plant gives out root.
(3) Layered part can be separated from the parent plant & grown into a new plant.
Examples :- Rose, Jasmine, Strawberry, grape vine etc.
Detailed Method of Layering –
- From a flexible lower branch, leaves are removed.
- Bent to ground level & conversed with 5-8 and moist soil.
- The top of branch should be above the ground another method of layering-
- A notch of 2-3 cm cut is made by removing back of stem at its base
- The cut surface is covered with moist soil and wrapped with polythene & tied at both the ends.
- In the cut protein, roots arises with in 4-8 weeks.
- The rooted portion is separated from the parent plant & its planted.
Artificial Layering – Lemon, Guava, Hibiscus, bougainvillea, Jasmine, Mogra & many other ornamental plants.
Natural Layering – Raspberry, Strawberry etc.
GRAFTING– Grafting is a method in which two parts of different plants are joined together in such a way that they will unite and grow as one plant.
Scion– The upper part (stem) of the plant which is grafted on other plant.
Stock – The lower part (root) of the plant in which grafting is performed.
Steps of Grafting
- Selection of Scion & Stock
- Scion & stock are tied together in such a way that cambium of stock and scion showed crane in contact example of grafting several orange, lemon, luine & grape fruit can be grafted over citrus root stock.
Significance – Vegetative propagation is a method of raising plants which
- do not produce viable seeds
- Produce very few seeds, e.g Banana, Pineapple, orange, grape, rose etc
Parthenogenesis– This is defined as the process of development of an organism from an unfertilized egg.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
1 Two parents are involved
2 Off springs show the characterstics of the both the parents.
3 Take place in all higher plant and animal
Unisexual Bisexual & Hermaphrodite
- The organism in which The organisms in which male & female
male & female sex organs are present in same individual
are present in different individuals
- Usually are Animals Usually all plants and curtain animals like
- Tapeworm, Earthworm, starfish etc
Primary Sex Organs – Main organs which help in reproduction by forming sex cells or gametes.
Primary Sex Organ
Males – 2 Testis Meiotic division Sex Cells Sperms
Females- 2 Ovaries Meiotic division Ovum (Ova)
Fertilization – The process of fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete is called fertilization.
As a result of fertilization Zygote is formed which develops into a new organism
Fertilization is of two types :-
External Fertilization Internal Fertilization
When fusion of gamete When spores are transferred to the
take place outside the body the reproductive system of female
of organisms through copulation & fertilization take
place in the body of female.
Copulation –The process of transferring sperms to female reproductive system & the structures associated with this process are called copulatory organs or accessory sex organs.
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction Over Asexual Reproduction–
1) Since fusion of gametes takes place from two parents, it causes diversity of characters in off springs
2) New Combination of Characteristics leads to
1) Origin of new species
2) Necessary for evolution to occur
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Reproductive part of higher plants – Flower
Various Parts of a flower
- a) Sepals – Green & Production
- b) Petals – Coloured & Showy
- c) Stamens – Male Reproductive part
- d) Carpels – Female Reproduction part.
Stamen – Stalk called filament + flodened top called anther.
Carpel :- Ovary + Style + Stigma
Pollination
Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination. Pollen grains are transferred by many agents such as wind, water, insects and other agencies. Pollination are of two types:
(i) Self Pollination
When the pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the same flower it is termed as Self Pollination or autogamy. For example : pea and china rose.
(ii) Cross Pollination
The transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the different plant of the same species in Cross Pollination.
Fertilization in Plants
The fusion of male and female gametes is known as fertilization. During fertilization the following events take place.
- The inner wall of each pollen grains germinates into a pollen tube that grow down through the style and finally reaches the ovule through small opening micropyle.
- The pollen tube contains two male gametes. The pollen tube releases the two male gamete into embryo sac which contains the egg.
- One male gamete fuses with the egg cell forming a diploid zygote. This is termed as Fertilization (Syngamy).
- The second male gamete fuses with the fused nuclei of two polar bodies (Secondary polar nucleus) and triploid endosperm mother cell is formed known as triple fusion. Endosperm mother cell divides mitoically to form endosperm.
- The process in which one male gamete fuses with the egg and the other with secondary polar nucleus is known as double fertilization.
Post Fertilization Changes
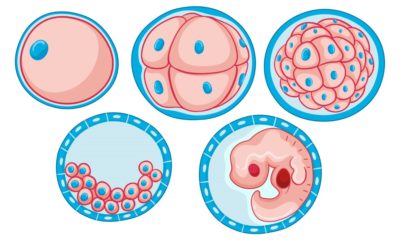
- Zygote divides many times to form the embryo.
- Endosperm mother cell forms the endosperm of seed.
- The sepals, petals, stamens, style and stigma of the flower wither and fall off.
- The ovary grows rapidly to form the fruit.
- The ovule change into seed.
Reproduction in human beings
- Human beings are unisexual
- There is distinct sexual dimorphism i.e. males are visibly different from females in physical build up, external organs and accessory (external) sexual characters.
- The structures associated with reproduction are different in males and females.
- The structures associated with female reproduction constitute the female reproductive system and the structure associated male reproduction constitute the male reproductive system.
The reproductive systems of males and females consist of many organs which are distinguished in to primary and secondary sex organs.
Primary and secondary sex organs
Primary sex organs – The organs which produce sex cells. (or gametes), and secrete sex hormones are called primary sex organs or gonads.
Male gonads – These are testes which produce sperms and male hormone testosterone female gonads :- These are ovaries which produce ova and female hormones- estrogen and progesterone.
Secondary Sex organs:- The secondary sex organs include the genital ducts and glands which help in transportation of gametes and reproductive process. They neither produce gametes nor secrete hormones. Penis and Vagina are Secondary sex organs.
Primary Sexual Characters:- Primary sexual characters are those present of birth.
Secondary Sexual Characters:- The secondary sexual characters are those that develop at puberty.
Puberty:- Puberty is the age at human males and females at which the reproductive organs become functional , gonads start producing gametes and sex hormones, and the boys and the girls become sexually mature.
Puberty in males:- It is attained between the age of 13 to 14 yrs and is triggered by the secretion of hormones – testosterone from testes.
Puberty in females– It is attained between 10 to 12 years and is triggered by the production of the hormone- estrogen from the ovaries. This hormone brings about the growth and maturation of the reproductive tract and the development of secondary sexual characters. Puberty changes a girl child in to a woman fit to bear children.
Secondary Sexual characters in human males.
- Enlargement of penis & scrotum.
- Broadening of shoulders and increased muscle development.
- Enlargement of larynx and thickening of vocal cords producing deepening of voice.
- Growth of public hair and extra hair on the face, in the armpits and on the chest.
- Changes in behavior associated with courtship and mating.
- Increase in height.
Secondary sexual characters in human females
- Growth of breasts and external genitalia (vulvas)
- Growth of public hair and extra hair in armpits.
- Hair on beard, moustache and chest are lacking
- Broadening of pelvis.
- Initiation of menstruation and ovulation.
- Increase in subcutaneous fat, particularly in thighs, shoulders, buttocks and face.
Male Reproductive System – Human male reproductive system consists of the following organs –
- Testes (Sing.- Testis):- These are the oval shaped primary reproductive organs in man. A pair of testis lies in a small sac like, muscular structure outside the abdominal cavity called Scrotum. The function of testes is to produce sperm and male sex hormone called testosterone. The scrotum provides the optimal temperature for formation of sperms.
- Epididymis:- It is a coiled tube-like structure firmly attached to the testis and server as the sore house of sperms. Inside the epididymis, sperms become mature and develops motility.
- Vas deferens:- The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens or sperm duct in to organs called seminal vesicles, where the sperms get nourished and stored.
- Urethra:- It is a common duct for the passage of both urine and spermatic fluid Urethra carries the sperms to an organ called penis which opens to the outside through a male genital pore.
Female Reproductive system:- The human female reproductive system consists of the following organs:-
- Ovaries:- These are a pair of small and oval shaped organs, located in abdominal cavity near the kidney. Ovaries the female primary reproductive organs, which perform dual functions of production of female gamete or ovum and the secretion of female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian tube or oviduct:- These are a pair of ling convoluted tubes that carry ova or eggs form the ovary to the uterous. The fallopian tube has a funnel shaped opening near the ovary. These tubes from both the sides open in to a muscular structure, the uterus.
- Uterous (Womb):- It is a hollow, pear shaped organ within which the embryo develops. Its upper portion is broader while its lower portion is narrower, called Cervix.
- Vagina:- The cervix opens into the vagina which is a tubular structure and also called “birth canal”.Vagina receives sperms from the male and also serves as the passage through which the fully developed foetus is born.
Sexual cycle in females:-
The human reproductive cycle is concerned with the sexual cycle of a woman, which begins at the age of definite intervals
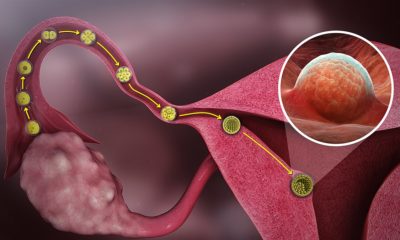
- The ovarian follicles grow in to mature follicles, and one follicle develops to form a mature ovum.
- The ovum is then released from the respective ovary by the process called ovulation
- At the time of ovulation fertilization ca occur.
- After ovulation the remaining part a the follicles secrets hormone- progesterone which stimulates the thickening of the uterous wall.
- The breakdown of the inner, thick and soft, lining of the uterous along with its blood vessels in the form of vagina of bleeding is called menstrual flow or
- The cycle of events taking place in the ovaries and uterous every twenty eight days and marked by the menstrual flow is called menstrual cycle or sexual cycle in human female.
- Menstruation occurs every 28 to 30 days and ovulation takes place in the mid of the menstrual cycle around 14th
- Bothe ovulation and menstruation stops temporarily when the women gets pregnant till birth at the offspring.
- The beginning at menstruation at puberty is called menarche.
- The age at which the menstruation stops and a women loses her ability to bear children is called menopause.
- The period between menarche and menopause (i.e. 10-12 yrs to about 45-50 yrs.) is the normal reproductive life of a woman.
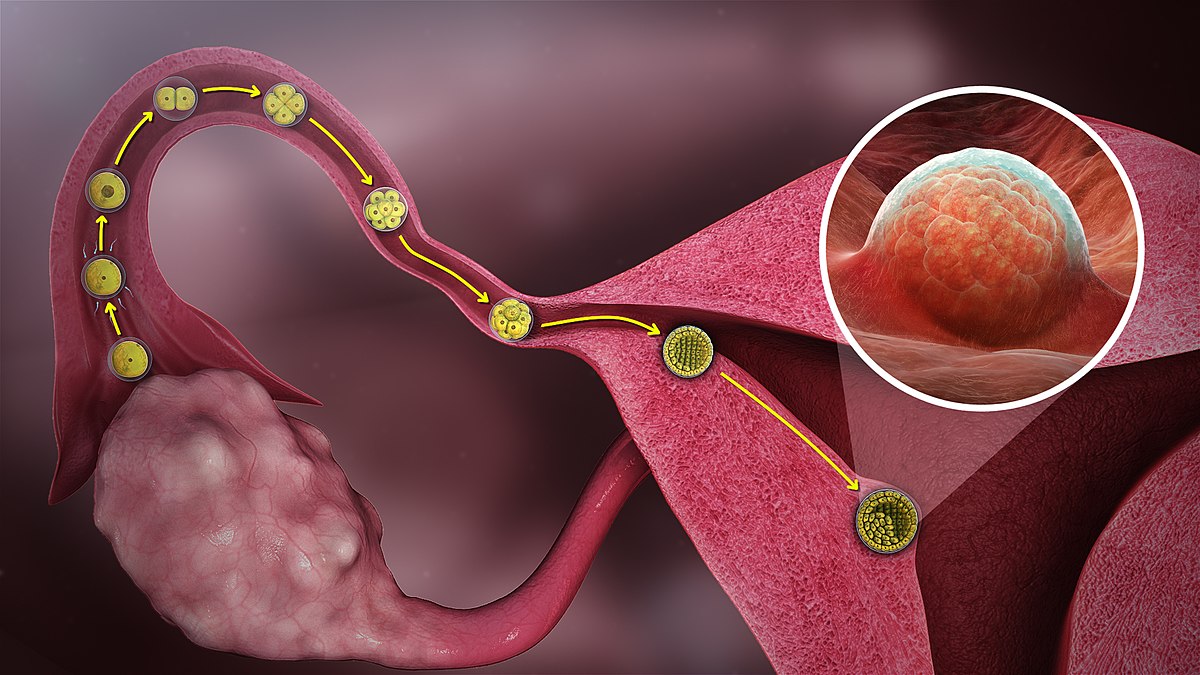
Fertilisation:-The fusion of sperm nucleus with egg nucleus to form a diploid zygote is called fertilization.
- fertilization is internal in human beings
- The male gamete is introduced inside the female genital tract (Vagina) by the process of copulation or mating.
- Sperms are highly active and mobile which move up through cervix into the uterus and then pages into the fallopian tubes.
- In the fallopian tube only one sperm fertilizes the ovum to form zygote. This is called fertilization.
- fertilization occurs only if copulation takes place during the ovulatory period.
Post fertilization changes
- After fertilization the embryonic development of the zygote starts immediately in the fallopian tube and pregnancy starts while menstruation stops.
- The embryo moves down to reach the uterous. The embedding of embryo in the thick inner lining of the uterus is called
- Then, a special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo (foetus) Called placenta, where the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products takes place.
- The time period for the development of foetus inside the uterus till birth is called
- The act of giving birth of the fully developed foetus at the end of gestation period is termed as parturition.
- The average duration of human pregnancy is about 40 weeks or 286 days.
Population Control
Population is increasing day by day thus we need to control it, for this a number of preventive methods or devices have been developed to prevent the conception (i.e fusion of male gamete with female gamete) and broadly Categorized as:-
(1) Barrier Methods:- In that method some physical devices are used to prevent the entry of sperm in the female genital tract during copulation. They also protect sexually transmitted diseases (STDS)
Ex- Condoms, Femi Dom, diaphragm (Cervical Cap)
(2) Chemical Methods:- foam tablets, jellies, pastes, creams and spermicides are some common chemicals used by woman for preventing ovulation or for killing sperms.
Ex- Oral Pills:- These are used to check ovulation
Vaginal pills:- These are drug preparations which contain spermicides. These are used be for copulation by women.
(3) Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD):- These are contraceptive devices made of copper, plastic or stainless steel. These are used to prevent implantation, in the uterus.
Ex- copper-T, Loop, Spiral ring, bow and shield.
(4) Natural methods:- Avoid copulation around the time of ovulation and withdrawal of penis before ejaculation are some natural methods which are helpful in preventing unnecessary pregnancy.
(5) Surgical Methods:-
(i) Castration:- Removal of testes in male.
(ii) Ovariectomy:– Removal of ovaries in females.
(iii) Vasectomy:- Cutting of vas deferens and tying the cut end to prevent the entry of sperm in urethra.
(iv) Tubectomy:- Cutting of fallopian tube or oviduct.
Reproductive health
It is all those aspects of general health which, help a person to lead a normal, safe and satisfying reproductive life.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS)
The infections (communicable) diseases, which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person by sexual, contact are called sexually transmitted diseases.
- The human beings suffer from over 30 different kinds of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). They are usually caused by bacteria, protozoa and viruses.
The common STDS are as follows-
- Gonorrhia:- It is caused by bacteria Nisseria gonorrhea. It is characterized by inflammation of urino genital tract and the patient feels burning sensation during urination. This bacteria infects the ureter in men and cervix in women.
- Syphils:-It is caused by bacterium. Treponoma pallidium. It is characterized by lesions in the mucous membrane of urinogenital tract and ulcers on genitalia.
- Trichomoniasis:-It is caused by protozoan Trichomonas Vaginalis. It is characterized by some vaginal discharge at the urinogenital tract of the female.
Another sexually transmitted disease is AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). It is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).